
EMDA for the Treatment of NMIBC
What is EMDA®
EMDA®, Electromotive Drug Administration, is a device-assisted therapy that increases drug transport across biological membranes under the influence of an electric field
EMDA® is characterized by a combination of different electromolecular interactions that improve drug absorption from 4 to 7 times:
- Iontophoresis
- Electrophoresis/Electroosmosis
- Electroporation
The deeper drug penetration and the greater drug bioavailability result in an increased clinical effectiveness
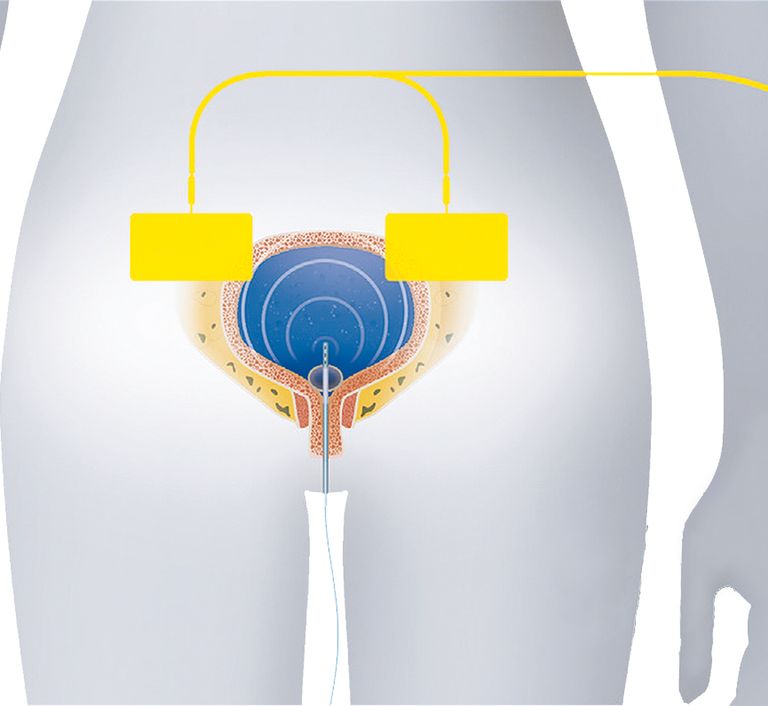
Treatment Modality
- Urogenic 16F electrode catheter is inserted into the bladder
- The bladder is drained to remove residual electrolytes
- The drug solution is administered
- Two dispersive electrodes are placed on the sides of the navel with an abundant layer of conductive gel
- A micro-current is applied for 20 minutes
EMDA® treatment is quick, easy to use and safe
WHY EMDA®
A unique technology to augment the effect of intravesical chemotherapy by creating an electric field across the bladder wall which increases urothelium’s permeability
- The Physion EMDA® system has been proven excellent results in treating high-risk and intermediate-risk patients with non-muscle invasive bladder cancer.
- EMDA® + Mitomycin treatment is an efficacy tool in the long-term conservative strategy of high-risk unresponsive to BCG as a “bladder sparing” therapy.
- Several thousand treatment cycles have been performed with complete safety following TURBT: significantly reduced recurrence and progression with increased disease-free interval.
- EMDA® can be used with all types of Mitomycin and in sequential treatment EMDA® + Mitomycin is combined with BCG.
- More data on EMDA® now available than any other device-assisted drug delivery system available.
- Proven deeper tissue penetration of Mytomicin with EMDA® compared to passive administration.
- In according to EAU Guidelines 2021.
Electromotive drug administration
The efficacy of MMC using electromotive drug administration (EMDA) sequentially combined with BCG in
patients with high-risk tumours has been demonstrated in one small RCT [300]. The definitive conclusion,
however, needs further confirmation. For application of device-assisted instillations in patients recurring after
BCG treatment, see Section 7.9.3.

Bladder Cancer Protocols
Discover more about our extensive range of professional services. We constantly update this page, but if you still can’t find what you’re looking for, please feel free to get in touch with us – we will be more than happy to help.

INTERMEDIATE-RISK NON-MUSCLE INVASIVE BLADDER CANCER

SINGLE INTRAVESICAL INSTILLATION OF EMDA-MITOMYCIN BEFORE TURBT

INTRAVESICAL SEQUENTIAL ADMINISTRATION OF BCG AND EMDA-MITOMYCIN IN HIGH-RISK NMIBC

BCG FAILURE PATIENTS
EMDA for Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer
List of Publications















